
Synergy: Strategy & Brand
Brand Development
A brand is essentially the customer’s perception of an organisation, product, or service. It comprises physical representations, such as logos, advertising, and taglines, as well as the customer’s own experience through actual contact with the organisation or awareness of its reputation. Brands are one weapon in an organisation’s strategic arsenal.
A strong brand can differentiate a product, target a market, build stakeholder relationships, increase organisational influence, lay the foundation for pricing premiums, or develop investor confidence. It can also increase the consumer’s trust in a product or service, expediting acceptance or take-up.
When utilised for its highest value, the brand will support the achievement of the organisational strategy. There will be strong links between the organisation’s brand, the overall strategy, and market-facing strategic initiatives.
Like the development of strategy, the process of developing a brand can be planned or ad hoc. An organisation choosing to build its brand strategically will typically follow a process that begins with brand identification and continues through brand management. To maximise brand penetration and value, organisations will focus on increasing brand engagement.
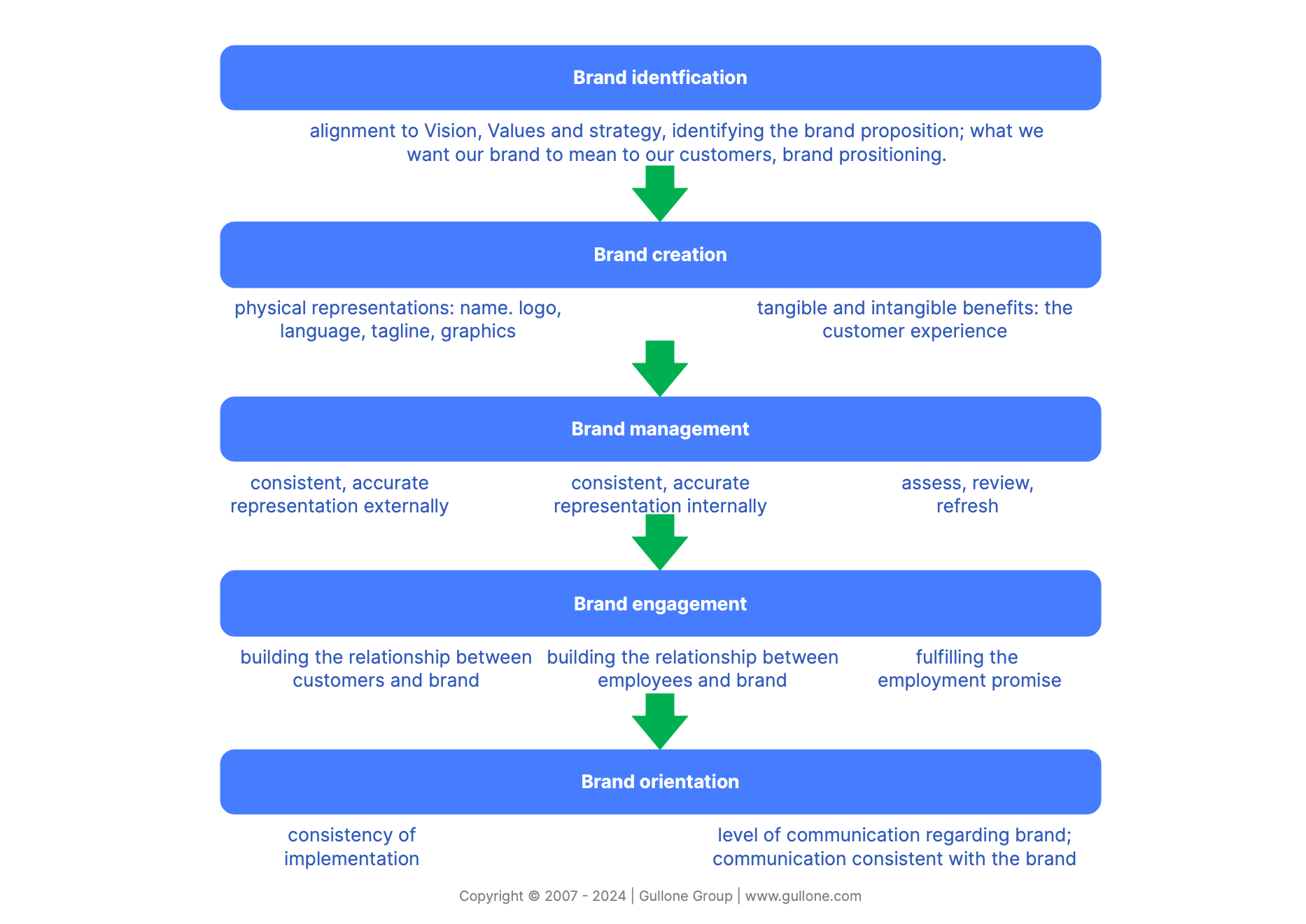
Brand orientation is the level to which the organisation itself is attuned to the brand, the level of attention the brand receives internally, and the consistency with which it is applied.
It is vital to understand that the more relevant the concept of ‘trust’ is to an organisation’s success, the more critical ‘brand’ becomes. Highly trust-dependent industries include those that supply emergency services, those that sell products and services of a personal nature or goods for consumption by children, and those dealing with sensitive personal information.
A highly trust-dependent organisation usually charges a premium for its products or services, is highly dynamic, and moves quickly within its markets. It might also seek to address some form of negative perception from the past. In all of these circumstances, strong brand development and management are essential if the organisation is to consistently perform at a high level.
The concept of branding is ideally considered throughout the development of a strategic plan. Strategic plans do not replace a cohesive branding or marketing strategy, but they should align with the existing brand or interface with the development of a new brand. This article explains how brand and strategy interact so they are both developed and managed for the greatest effect.
Phases
1. Brand identification
In this process, the organisation settles on the identity of its brand. It defines its DNA, if you will.
Successful brands are usually defined by a combination of logical and emotional appeals to the customer, e.g. ‘fresh and exciting’, ‘polished, first-class and luxurious’, or ‘cheap, quick and easy’.
The organisation should first determine how the brand is currently perceived. Normally, this would involve brand recognition research, in which stakeholder groups are surveyed to understand how they perceive the organisation or its products and services. If the organisation has access to enough customer feedback, it might take a shortcut by conducting a SWOT analysis of the customer experience. It is important to reflect on the level of alignment between that customer feedback and the organisation’s Vision and Values.
At this stage, the organisation must determine if the current brand image (how the brand is perceived) meets the brand identity (how the organisation or product intends to be perceived). The brand strategy will need to include initiatives to meet any gap between organisational intent and stakeholder perception. If significant enough, these initiatives would also be included in the Strategic Plan.
It is much easier to leverage an existing brand image than to create a new one. However, change is sometimes necessary for an organisation to achieve its strategic goals. For example, if the current brand image includes public perceptions of faulty products or unreliability, the organisation can choose between addressing low production quality or accepting this as a product limitation that is offset by another benefit to the market, such as low cost. Strategically, this choice might be evaluated as selecting between a TQM production approach or filling the low-cost provider segment of the market. Either can be successful strategies, but they will lead the organisation to very different outcomes.
Finally, it is vital to ensure that the brand’s core values or features align with the organisation’s values. This avoids a culture hamstrung by conflicting efforts and priorities and ensures that both organisational and brand values can be consistently represented. For example, it is extremely difficult to create a fun and lively brand if staff are managed in a punitive and harsh fashion.
2. Brand creation
When the brand identity is decided, it must be created. At this point, the brand must manifest itself in the form of physical attributes and actions that will form the customer’s experience of the organisation. This has two aspects:
This has two aspects:
- Physical representations (i.e. brand name, logo, tagline, language style (or ‘attitude’) to be used in communications and graphics)
- Tangible and intangible aspects of the product or service that the customer will experience
The Strategic Plan should contain numerous actions that will change (or at least influence) the organisation's products and services. Any market-facing initiative would consider branding in its development or review. Even without a stamped logo, the core values of the brand would be reflected in the manifested product or service. For example, a service might be luxurious, attentive, brisk, or cheap.
Considering the brand during the conceptualisation and throughout the implementation of market-facing strategic initiatives will support brand management, delivering the right customer experience, and developing the organisation’s reputation.
3. Brand management
This phase aims to ensure that the brand is managed effectively. Branding should be applied consistently, frequently, and accurately. Emphasis should be placed on living up to the brand promise to ensure close alignment between brand identity (the brand that the organisation communicates) and brand image (how customers perceive the brand). This requires feedback mechanisms and any targeted improvement activities that may be required.
Communication of the organisation’s strategy forms part of the brand management process. Explaining the Vision and strategy to key stakeholders increases trust and a sense of partnership.
Communication needs to be consistent and an accurate representation internally and externally.
4. Brand engagement
Beyond managing the brand, the organisation can act to increase engagement with the brand. This occurs with both external and internal stakeholders. In this phase, the emphasis is placed on encouraging stakeholders to work with the brand, respond to it, use it, talk about it, feel a sense of community with it and even take up the opportunity to influence the organisation in some way, e.g. ‘Suggest a new drink flavour’, customer competitions, etc.
The development of social media creates an opportunity to dramatically increase engagement. The organisation may choose whether to limit its social media involvement to responsive customer service (managing a Facebook page, Twitter, and responding to customer service review sites) or actively stimulate customer feedback and participation. With either option, communications must be strongly aligned with the brand (e.g., friendly vs. cool, professional vs. casual, prompt vs. relaxed).
When reviewing the Strategic Plan, consideration might be given to actively engaging customers, other stakeholders, and employees with the brand, allowing them to participate in the evolution of the organisation’s products and services experience.
Various initiatives might be considered for inclusion in the Strategic Plan, or as part of business-as-usual operations. Strategic Plans might include:
1. Build the customer/brand relationship
- Marketing and sponsorships
- Promoting sustainability initiatives
- Community consultation
- Interaction with government agencies/networks/partners/alliances, etc.
- Social media/website interaction / Use of AI
- Customer feedback mechanisms
- Mechandising
- Interactive displays, competitions
- Developing marketing programs that encourage customers to interact with each other in a positive manner about the brand, product or service
2. Build the relationship between employees and the brand
It is vital to include employees in the overall development and management of the brand. Employees are responsible for delivering much of the customer’s experience. Ensuring that employees understand the brand assists them in ensuring their actions and behaviours are consistent with it. Providing employees with an opportunity to create positive change within the organisation contributes positively to staff engagement, which positively impacts their alignment with the brand.
Organisations can:
- Communicate the brand
- Communicate the Vision, Values and Strategy
- Create consistent organisational communication and presentation protocols
- Consult with staff
- Create customer service standards
- Utilise an effective performance management system
- Act on staff feedback
- Establish innovation / AI teams
- Establish internal 'SLAs'
- Conduct an internal customer survey
- Involve staff in the business planning process
3. Fulfill the employment 'promise'
Effective brand deployment involves ‘living the promise’. This applies to both customers and employees. Employees who see that their organisations have integrity (that is, that the leadership’s words are completely integrated with the organisation’s actions) can trust that the organisation will deliver on its promises. While it is vital to take positive actions, it is also important to announce an intention to do them beforehand. The alignment of communication and action creates trust and authenticity in the employer brand.
For some staff members, their employer's impact or standing in the wider community is a strong source of engagement or disengagement. Employees who are proud of their employer are more likely to be engaged and positively represent the brand externally (to ‘say, stay and strive’). Organisations must maintain or improve their reputations.
Strategic Plans can contain a number of actions that will support the fulfilment of the employment ‘promise’:
- Engagement survey and report
- Engagement strategy to build engagement to 'top employer' level
- Develop and retain high potential leaders
- Communicate strategy to staff and report progress against the plan
- Staff surveys
- Consistently deliver excellent service experience to internal customers
- Establish internal 'SLAs'
- Be seen as a supporter of the community
- Performance-based reward scheme across the organisation
- Offer training and development programs aligned with the strategic direction
- Ensure sustainability of the surrounding environment
- Develop a consistent performance management system
5. Brand orientation
Organisations keen to develop a strong brand will devote significant energy and attention to it. Brand orientation refers to the degree to which the organisation focuses on its brand. We consider it essential that all employees and customers have a clear perception of the brand and that it is consistently demonstrated. Still, the brand doesn't need to become a dominant feature of all staff communications or training.
We list the types of activities that might be considered in the drive to ensure a robust and consistent focus within the organisation on the brand:
- Communicate the brand
- Explain linkages between Vision, Strategic Plans, Values and brand
- Aim for a holistic experience of brand for all customers by ensuring stakeholder activities are aligned with the brand (as much as is possible)
- Engage staff in presenting their work in internal and external forums
Summary
It is advantageous to consider the implications of brand as the Strategic Plan evolves. This article outlines the linkages between strategy and brand and the potential for leveraging the brand for maximum strategic effect.
We work with our clients to identify those specific strategic objectives and initiatives that can be used to build on the effectiveness of the organisation’s brand. Brand can catapult organisational effort to ever greater levels of strategic and financial success.
Insights Article - Thought Leadership | gullonegroup | gullone.com | All Rights Reserved
